 What are the side effects of Lamictal? This question interests all patients with epilepsy and bipolar disorders. The information is divided into adverse reactions in patients with epilepsy and adverse reactions in patients with bipolar disorder. However, to consider the general safety of Lamictal (Lamotrigine), it is necessary to take into account the information of both sections.
What are the side effects of Lamictal? This question interests all patients with epilepsy and bipolar disorders. The information is divided into adverse reactions in patients with epilepsy and adverse reactions in patients with bipolar disorder. However, to consider the general safety of Lamictal (Lamotrigine), it is necessary to take into account the information of both sections.
Common side effects of Lamictal used for the treatment of epilepsy
Side effects related to skin and subcutaneous tissue
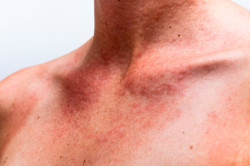 The most common Lamictal side effect is a rash, which usually appears during the first 8 weeks of the start of therapy and disappears after the drug withdrawal. There are reports of rare cases of severe, potentially life-threatening skin lesions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome).
The most common Lamictal side effect is a rash, which usually appears during the first 8 weeks of the start of therapy and disappears after the drug withdrawal. There are reports of rare cases of severe, potentially life-threatening skin lesions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome).
Although in most cases, when the drug was withdrawn, the symptoms disappeared, some patients had irreversible scars on their skin, and in rare cases, deaths related to taking the drug were recorded.
The overall risk of developing a rash as a Lamictal side effect is largely related to:
- lamotrigine overdose;
- interaction with valproate.
A rash can also be a sign of the hypersensitivity syndrome associated with various systemic manifestations.
You can see some of the lamotrigine side effects rash pictures in the right corner.
Lamictal side effects related to hemopoietic and lymphatic systems
- Hematologic disorders including neutropenia, leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis;
- Hematologic disorders may or may not be associated with hypersensitivity syndrome.
Lamictal side effects related to immune system disorders
- Hypersensitivity syndrome (including fever, lymphadenopathy, facial puffiness, blood disorders and liver function, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC syndrome).
Side effects related to nervous system disorders
- In monotherapy: irritability, headache; drowsiness, insomnia, dizziness, tremor, ataxia. One of the most common Lamictal side effects is anxiety;
- As a part of complex therapy: a headache, dizziness, irritability, nystagmus, tremor, ataxia, drowsiness, insomnia, aggressiveness, tics, hallucinations, confusion, agitation, instability, motor disorders, worsening symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, extrapyramidal disorders, choreoathetosis, increased frequency convulsive seizures, weight loss.
Visual disturbances
- Diplopia;
- Blurred vision;
- Conjunctivitis.
Side effects of Lamotrigine related to gastrointestinal disorders
- In monotherapy: nausea In complex therapy: nausea, diarrhea.
Hepatobiliary disorders
- Increased levels of hepatic enzymes, impaired liver function, liver failure. Dysfunction of the liver usually develops in combination with symptoms of hyperreactivity (in rare cases and in the absence of obvious signs of hypersensitivity).
Muscular and connective tissue disorders
- Lupus-like syndrome.
General disorders
- Fatigability;
- Another possible Lamictal side effect is depression.
What are the side effects of lamotrigine in the treatment of bipolar disorders?
Common lamotrigine bipolar side effects are the mentioned below:
- Skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- Nervous system disorder;
- A headache, agitation, drowsiness, dizziness;
- Disturbances of the muscular and connective tissues;
- Arthralgia;
- Pain in the body and limbs.
Lamictal and insomnia
People often wonder “can Lamictal cause insomnia“? Yes, it was proved that Lamotrigine has an effect on sleep. Studies with a small number of patients (10-15 people) showed that lamotrigine increases sleep stability (increases the duration of the fast sleep phase, reduces the number of phase transitions, and reduces the duration of the slow-sleep phase) and that there is no effect on vigilance, daytime sleepiness, and cognitive functions. However, in a retrospective study of the medical records of 109 patients, it was found that 6.7% of patients reported an increase in wakefulness resulting in insomnia, due to which treatment was discontinued. So we may conclude that lamotrigine and insomnia are two related things. If you take lamotrigine and notice insomnia, you’d better combine this medication with some light sleeping pills.
If you notice any severe lamotrigine side effects, contact your doctor as soon as possible. Hospitalization may be required. Always follow the instructions for use and do not exceed the dose of the medication.